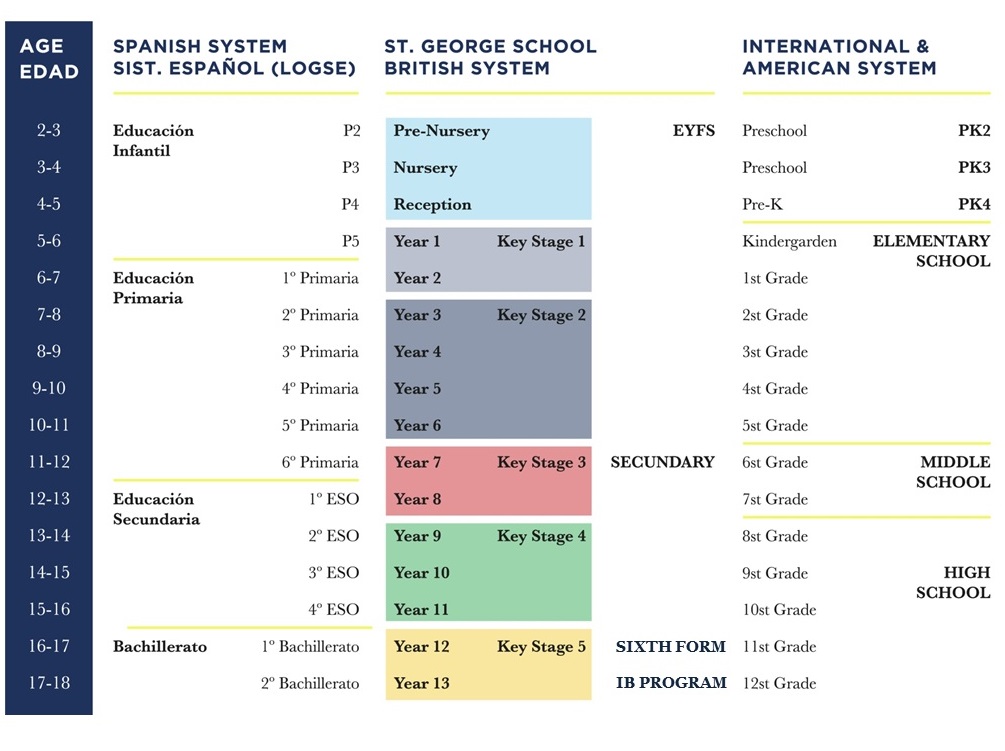
Our school follows the English National Curriculum and the last two years our students from 17 to 18 years old accomplish the IB Diploma program in English, in addition our students also take lessons in the subjects of Spanish Lengua and Sociales so that they can validate their studies with the Spanish system.